Project
Pelikan is a cache framework written in C. It provides an expanding collection of cache services, and a common library, ccommon, used to build them.
Pelikan optimizes for high-throughput, low-latency data access in a datacenter-like environment. It adopts a highly modularized architecture, and is carefully implemented to achieve high-performance and reliability at scale. Its design captures much of the commonality among similar systems, such as Memcached, Redis and Twemproxy, and makes improving and iterating on such services easier and faster.
Architecture
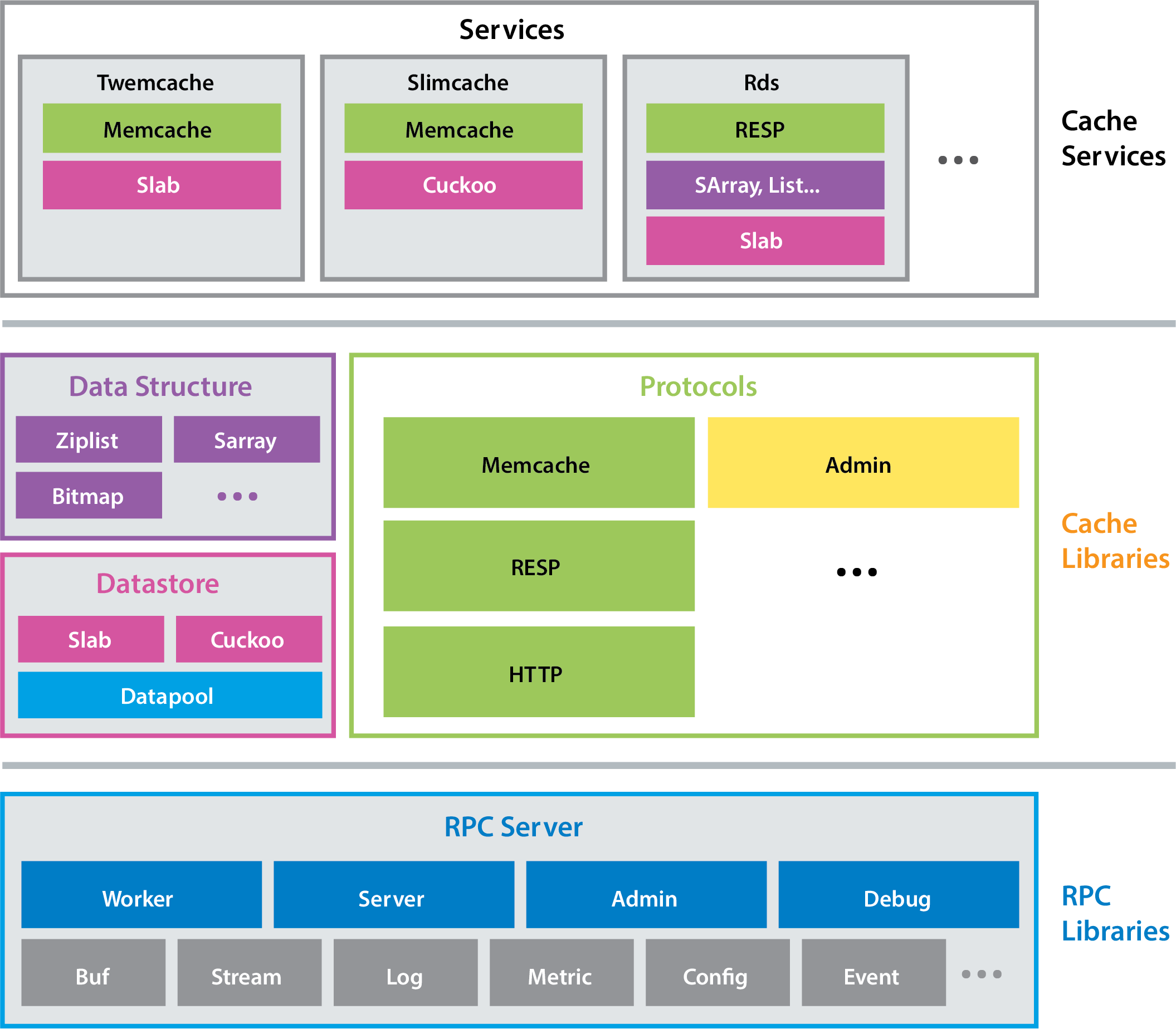
Pelikan Cache separates performance-sensitive processing from the less
performance sensitive processing, and it separates different types of
performance-sensitive processing from each other. Data request-response
processing and connection establishment are assigned to the data plane (the
“fast path”). Everything else is assigned to the control plane. Each major
processing pipeline gets its own thread— worker, server, admin, and
debug (see Figure 1).
Pelikan Cache brings several benefits to Twitter’s caching:
- Separation of control and data plane
- Data plane operations are guaranteed to be nonblocking, using lockless data structures to deliver low latencies
- Per-module configuration options and metrics that can be easily composed
- Multiple storage and API protocol implementations, and the ability to easily combine and extend them
- Low-overhead command logger that keeps up with full throughput and captures all request metadata for analysis
Products
Currently Pelikan yields three production-ready products, all of which are backends/servers.
pelikan_twemcache: a Twemcache replacementpelikan_slimcache: a Memcached-like server with ultra-low memory overhead- compared to Memcached/Redis, the per-key overhead is reduced by up to 90%pelikan_pingserver: an over-engineered ping server useful as a tutorial and for measuring baseline RPC performance
Community
- Join our chatroom on Zulip for questions and discussions
- Follow us on Twitter: @pelikan_cache
- Visit http://pelikan.io
Contributing
Please take a look at our community manifesto and coding style guide.
To get a sense of where things are going next, please visit our Roadmap wiki.
If you want to submit a patch, please follow these steps:
- create a new issue
- fork on github & clone your fork
- create a feature branch on your fork
- push your feature branch
- create a pull request linked to the issue
